Example: Fractional Factorial DOE
When to use this tool
Use the fractional factorial DOE to analyze the effects of multiple factors, each at two levels, on a numerical response. These designs are typically used when you have a large number of inputs and you want to screen out the trivial effects from the significant few that drive the desired output.
The advantage of fractional factorial designs is that they use a subset (fraction) of the full set of possible design runs to estimate the effects, so they are very efficient designs. The disadvantage is that they confound some effects in the process, so not all effects can be estimated. However, it is usually possible to select a fraction that gives the best information on the effects of interest while sacrificing the unimportant effects.
An Example Using EngineRoom
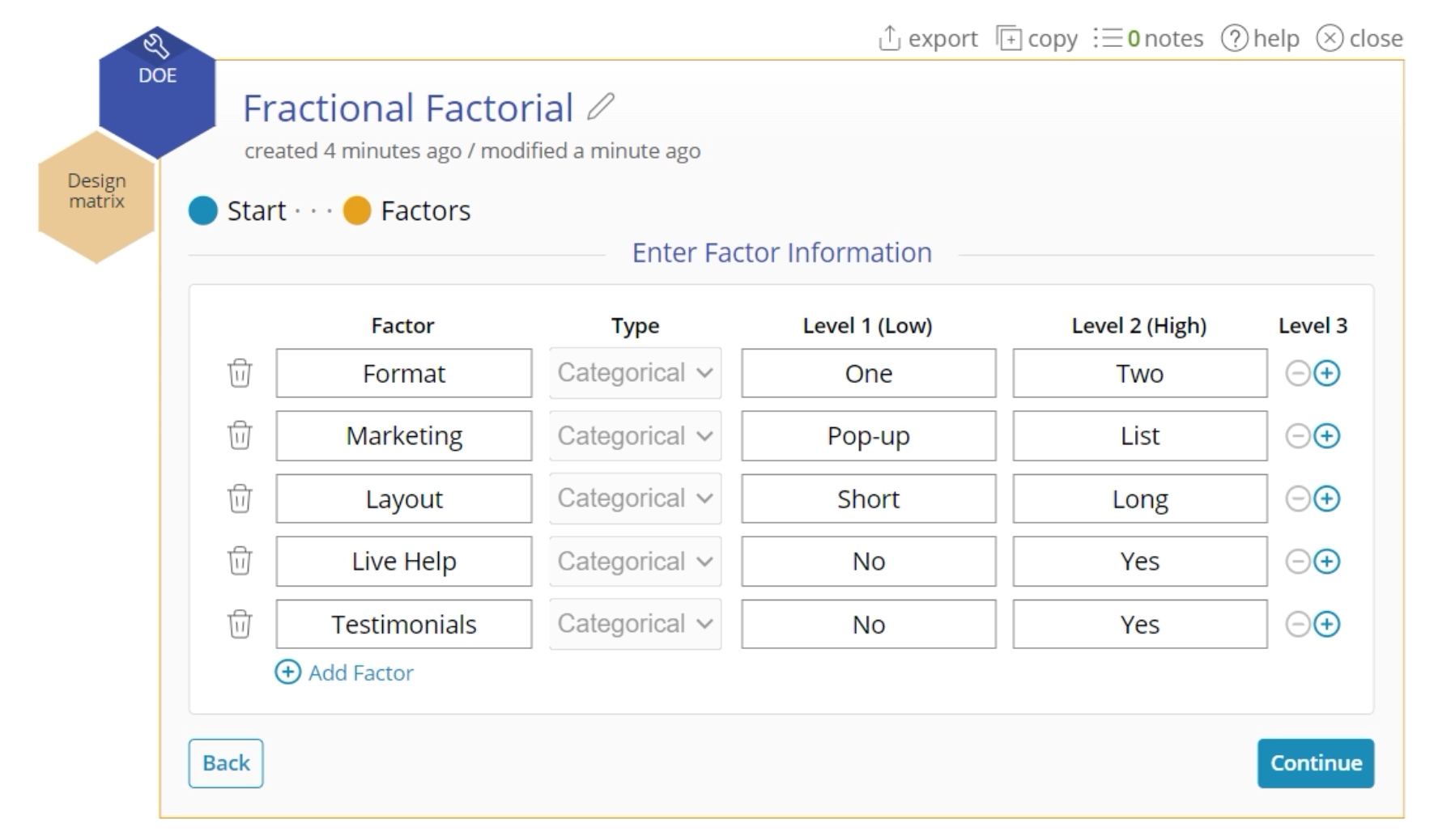
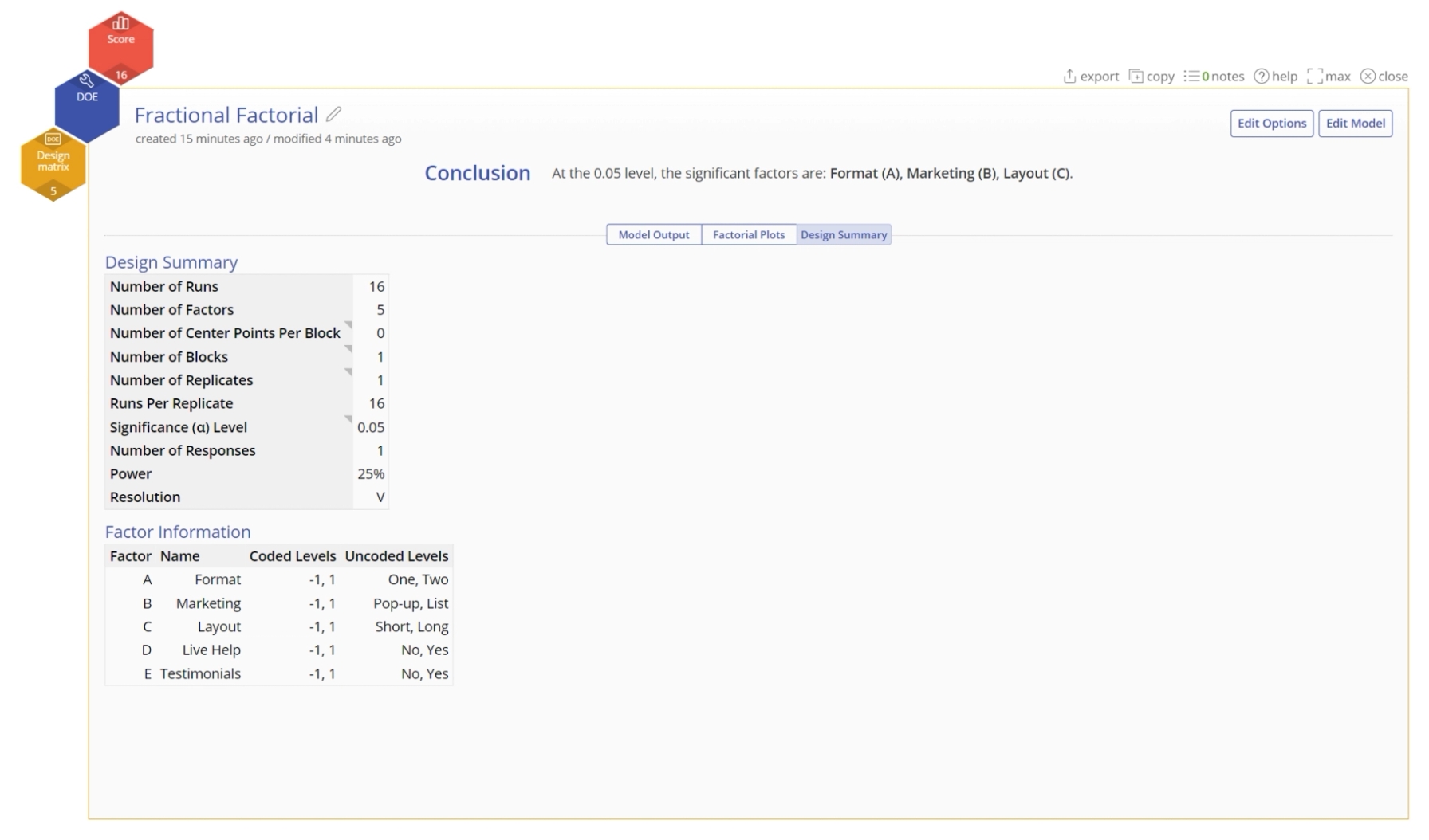
In this example, we will create and analyze a fractional factorial design to improve customer satisfaction scores with a website design. There are five factors under study, each at two levels:
- Color Format: One/Two
- Marketing Style: Pop-up/List
- Layout: Short/Long
- Live Help: No/Yes
- Testimonials: No/Yes
Steps:
1. Create Design:
- Open the DOE tool
- Select Start a design
- Add your factors from the study. Click the plus button to add additional factors.
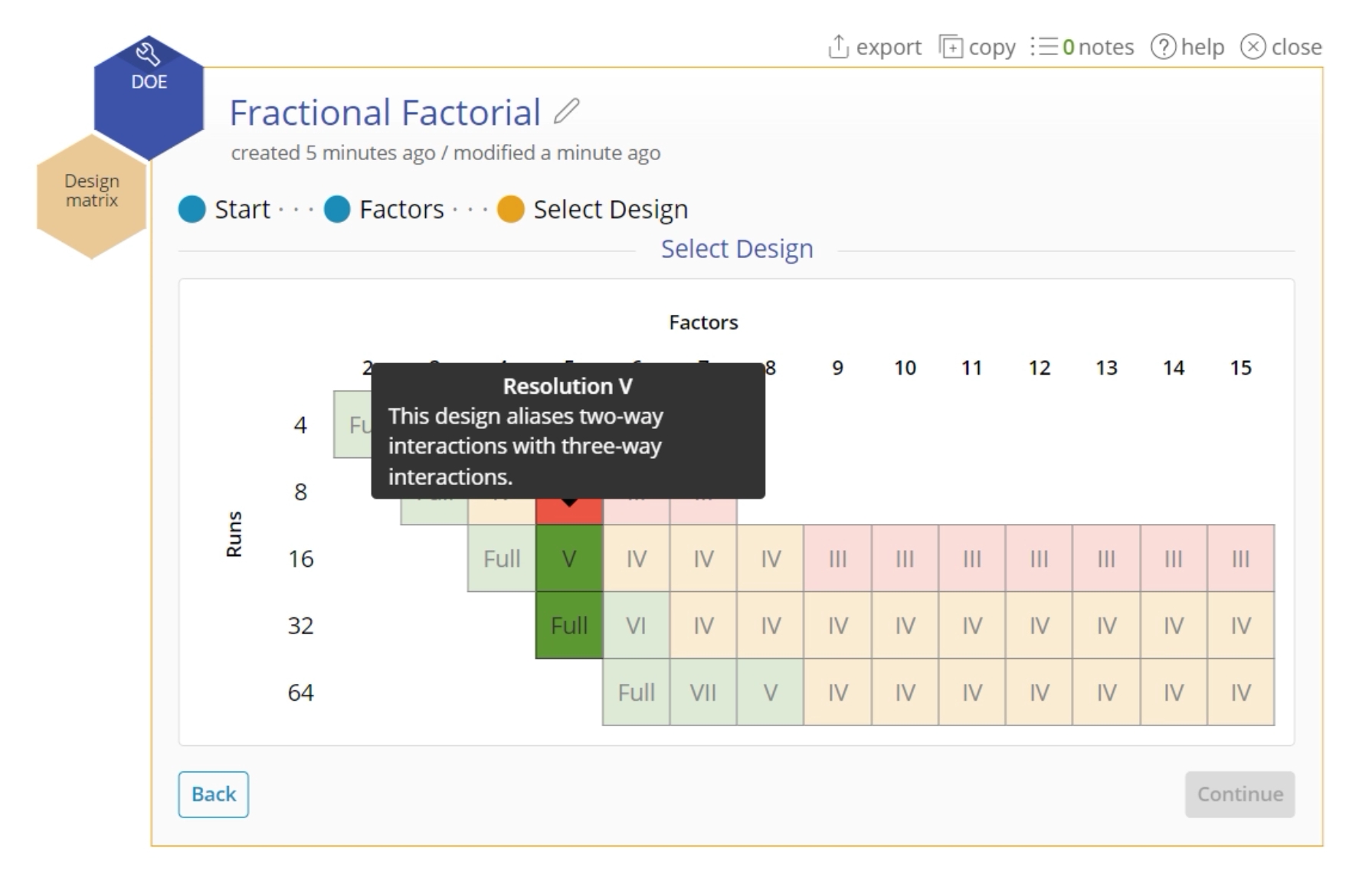
- Select the V design corresponding to 5 factors, which gives 16 runs:
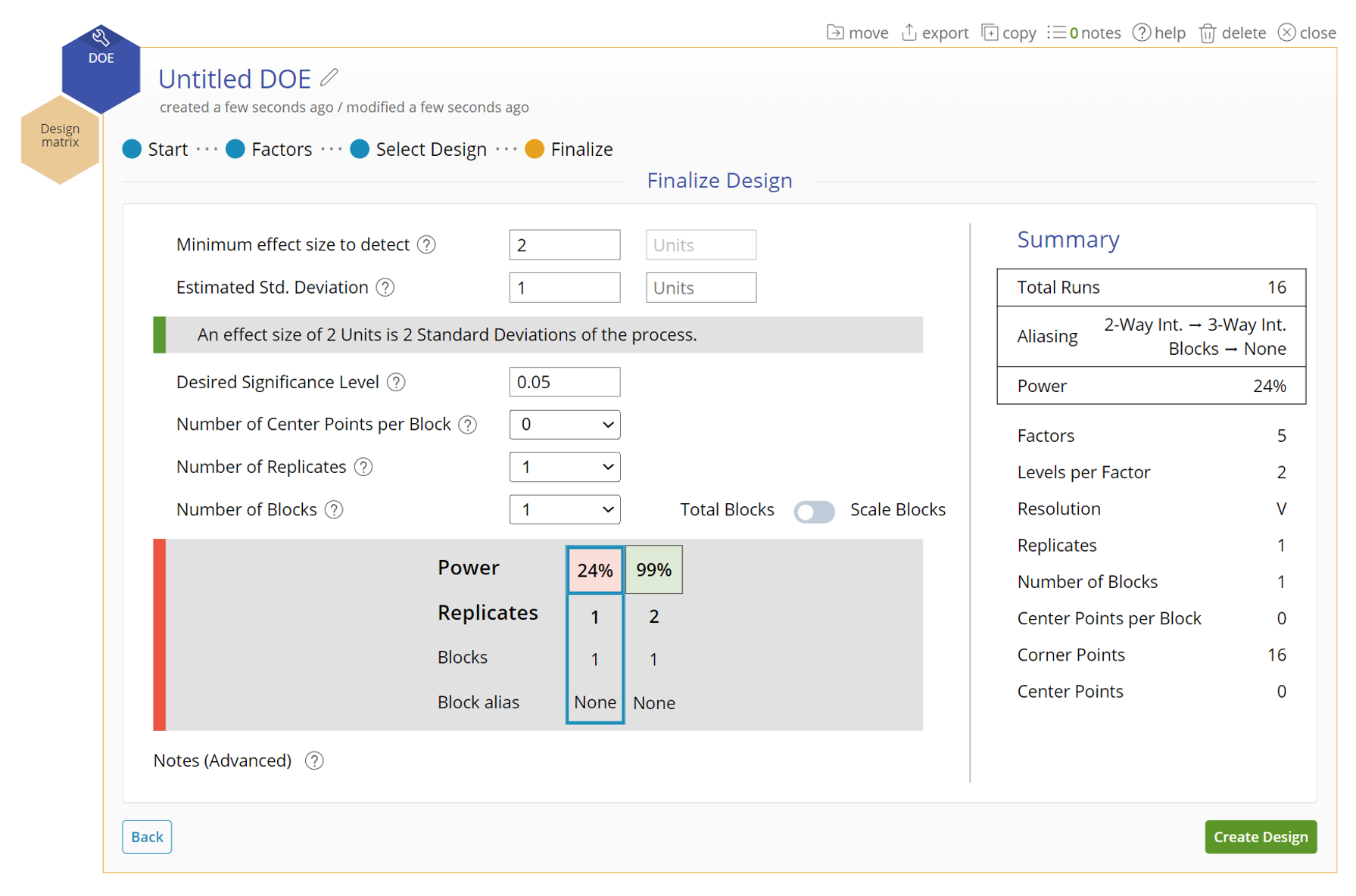
- We will leave the settings for finalizing the design at their defaults.
- Click Create Design.
2. Enter Data:
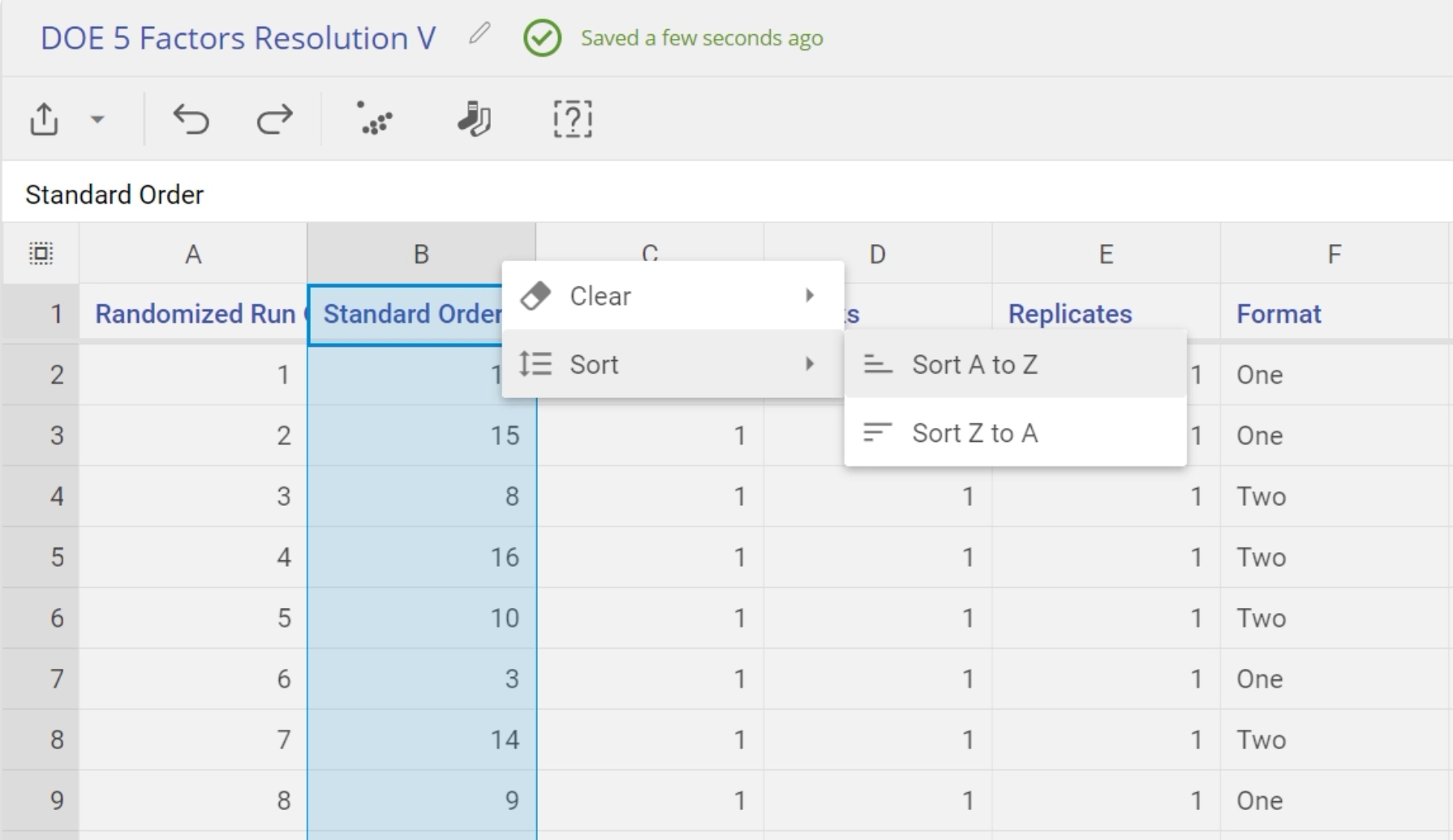
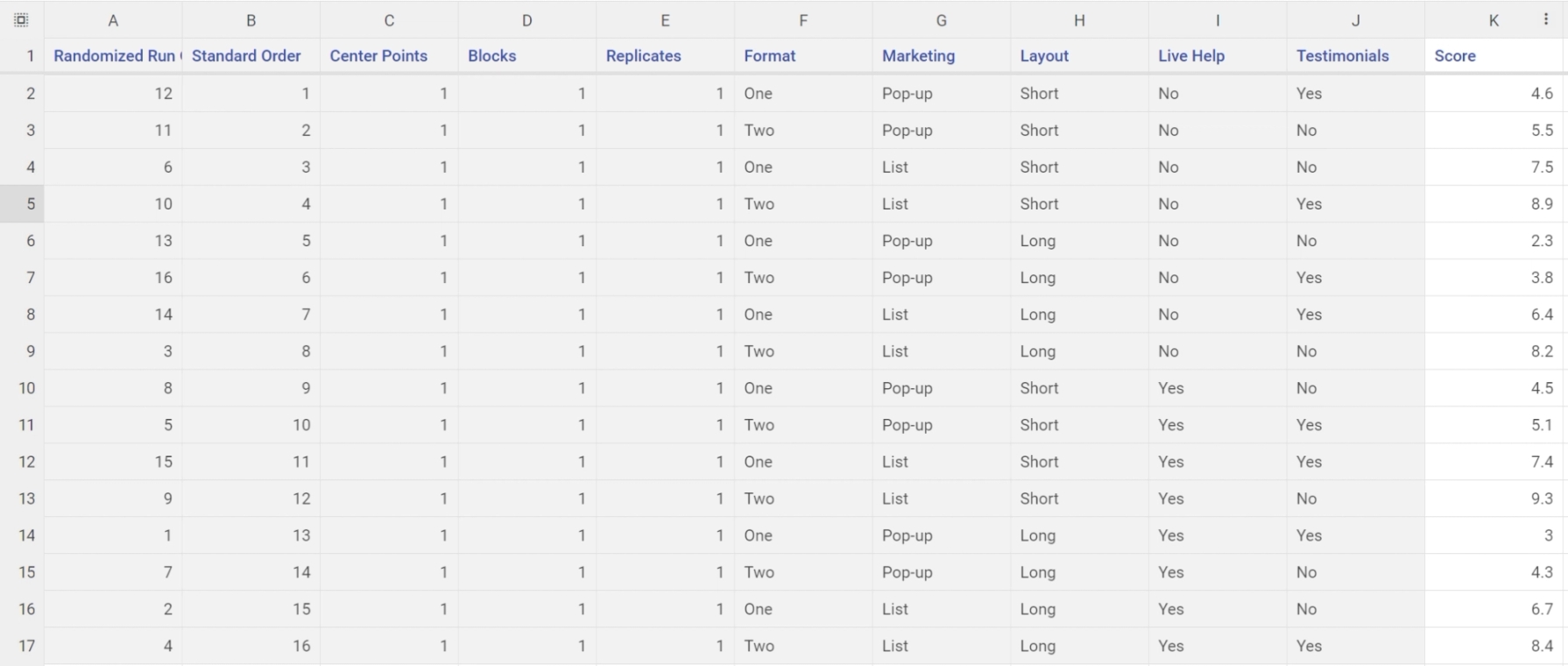
- The design matrix opens up from the data sources panel. It contains all the information about the design, with a blank column at the end; normally you would run the experiment by following the Randomized run order, and enter the response data into this column. However, since we already have the response data, we want to organize the table into Standard Order. This way we can simply enter or copy-paste the data, since the run order of both designs is identical (i.e., run #1 in the design we just created is the same as run #1 in the design table provided.) Sort the created design in the Standard order as well by right-clicking on the Standard order column, and clicking Sort > A -> Z:
- Copy-paste the response data into the blank column and click the "save and close" button:
3. Analyze Design:
Now it's time to analyze the design.
Note: If you need to change the design, you can click on the navigation across the top, or the Back button.
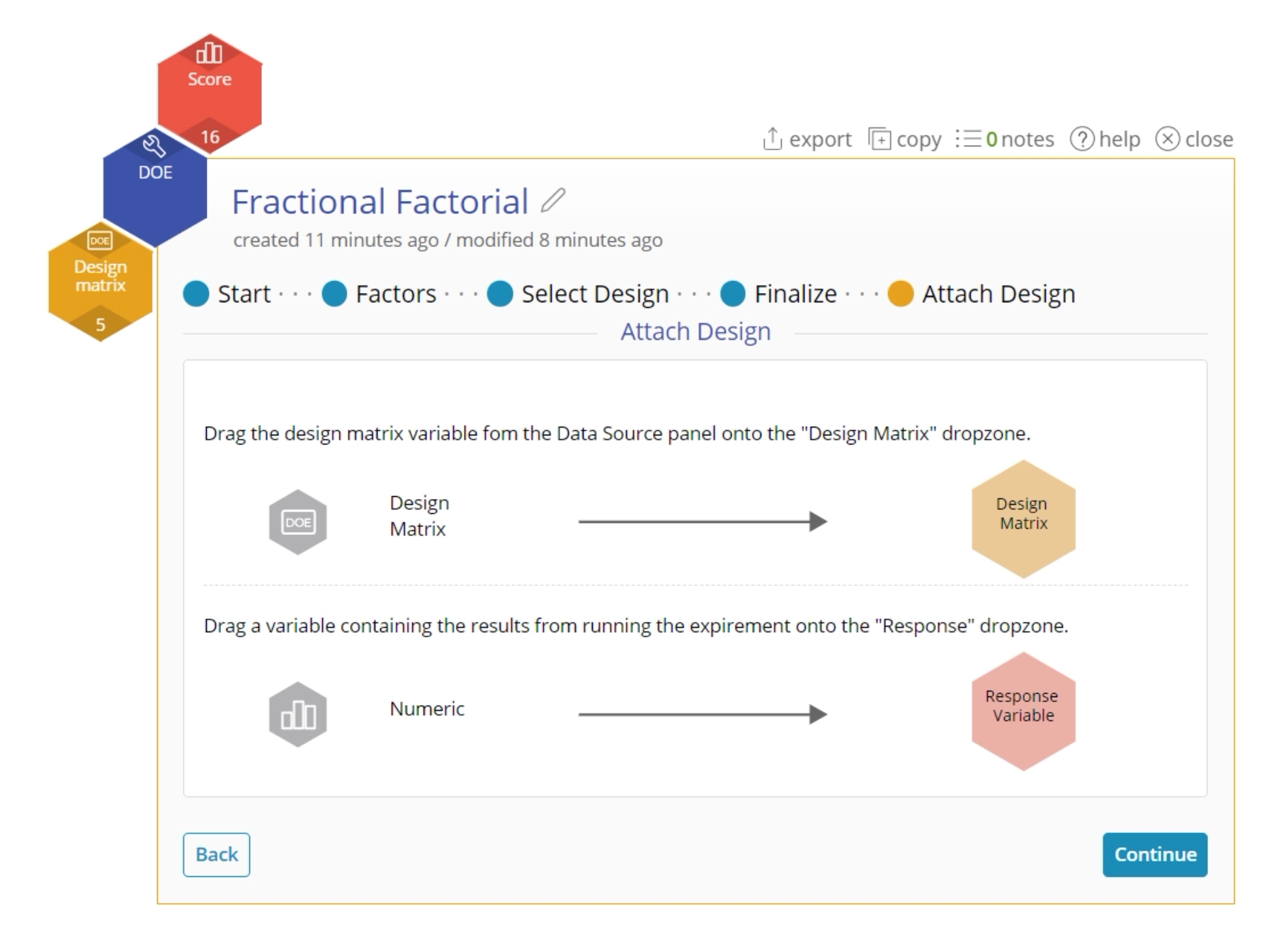
- Drag the Design matrix variable from the data sources panel onto the Design matrix drop zone, and the Score variable onto the Response Variable drop zone. Click Continue.
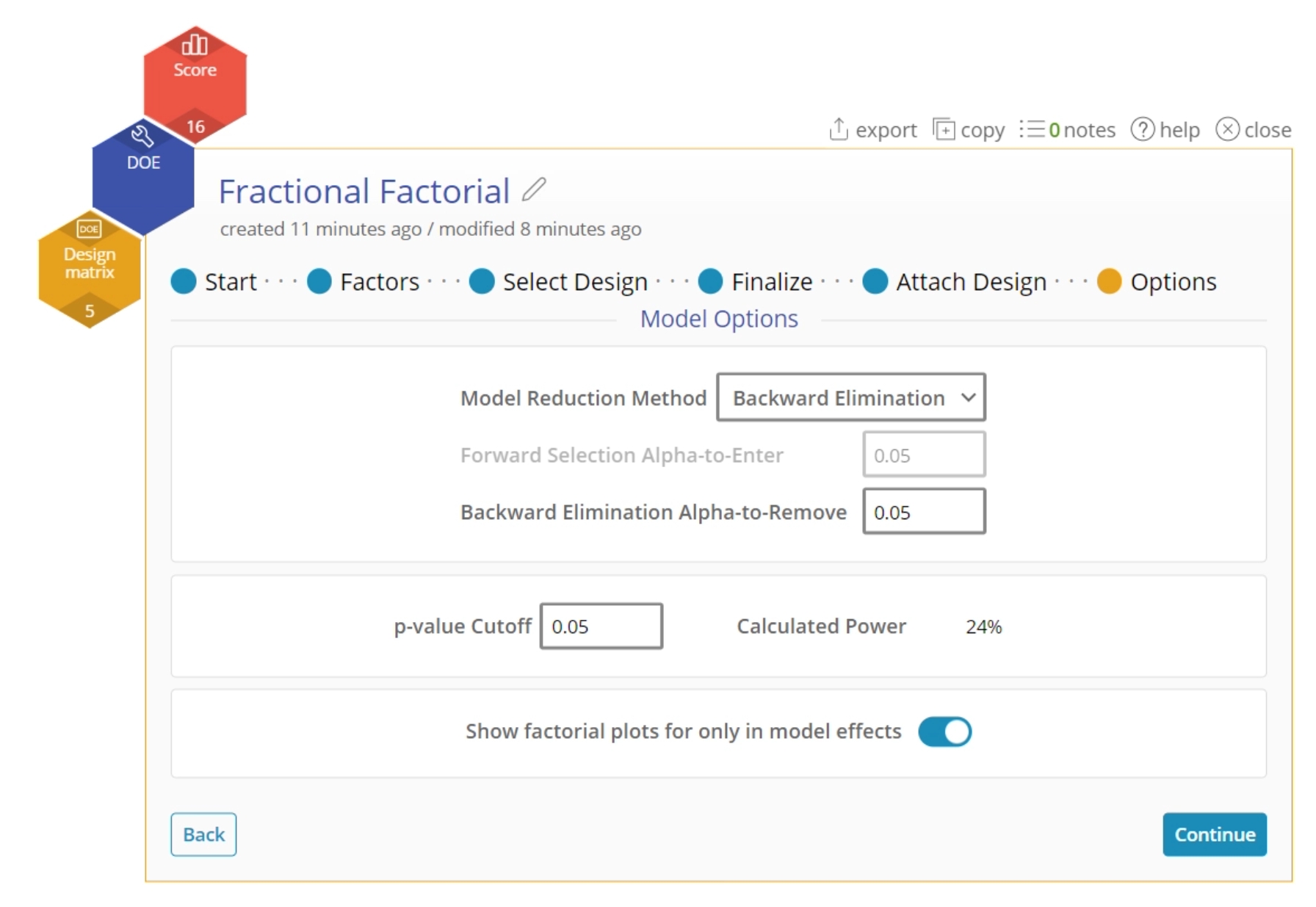
- Adjust any of the following parameters:
- Model Reduction Method: The default is to use Backward Elimination to reduce the model from full to the most significant factors. Other options include Forward Addition, Stepwise, and Manual Reduction.
- p-value: This option allows you to change the p-value after the creation of your design. You can see the new power calculated next to it.
- Show only Factors in Model: This has plots that only show within the model.
- Click Continue.
- The output contains several parts:
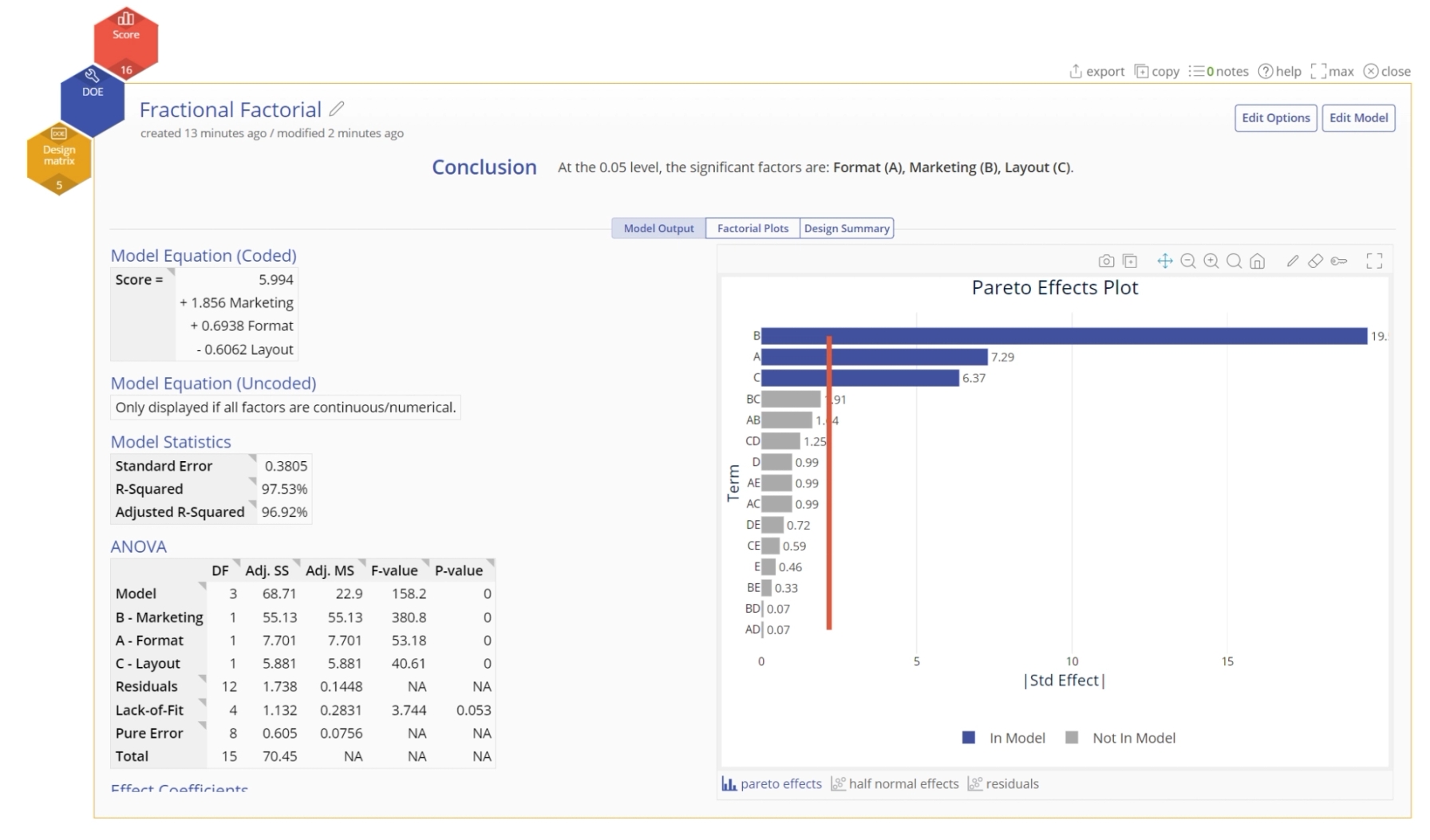
- Model Output Screen: This screen shows the resulting model equations and various factors the indicate the significance of an input.
Pareto effect plot:
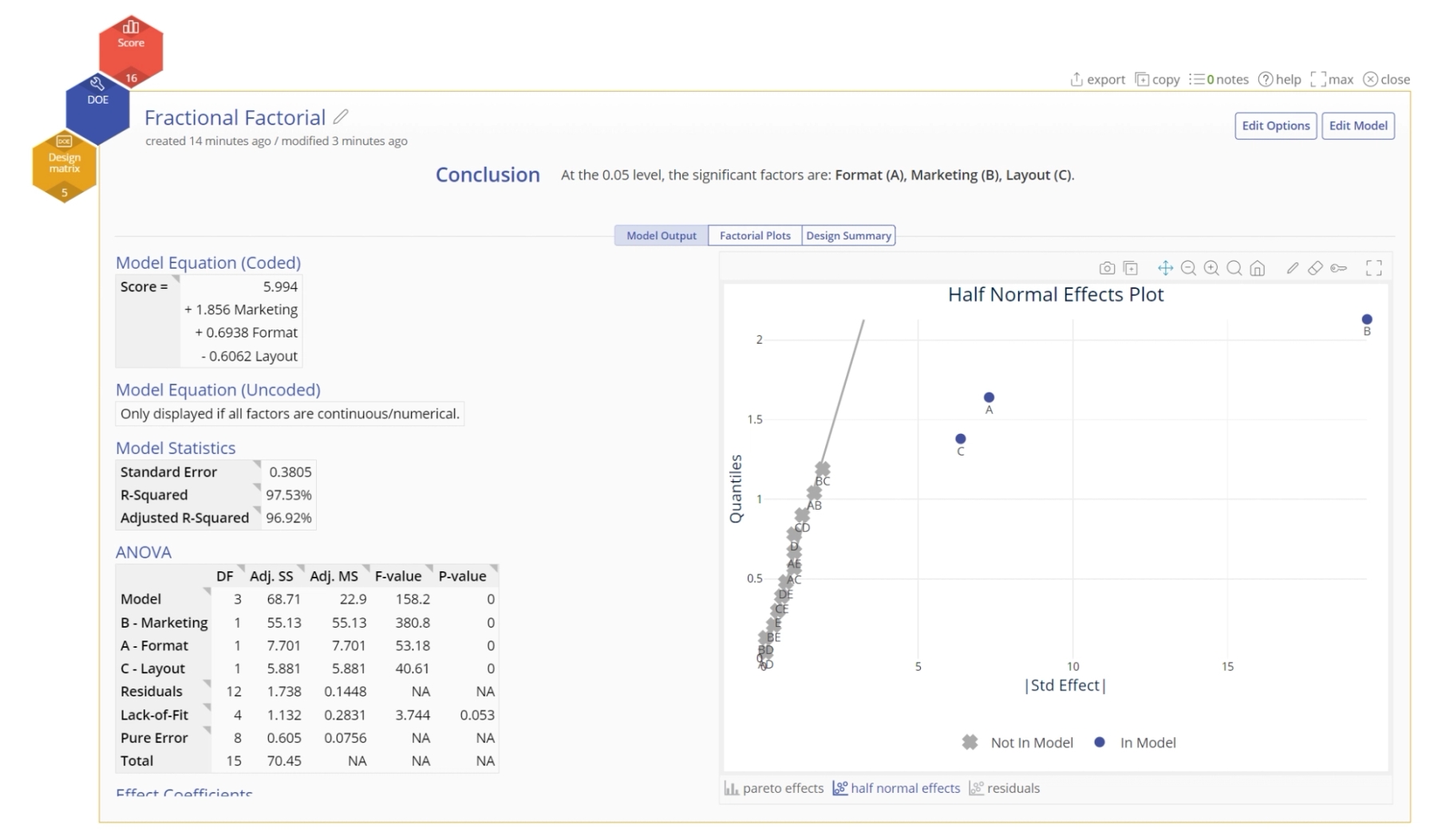
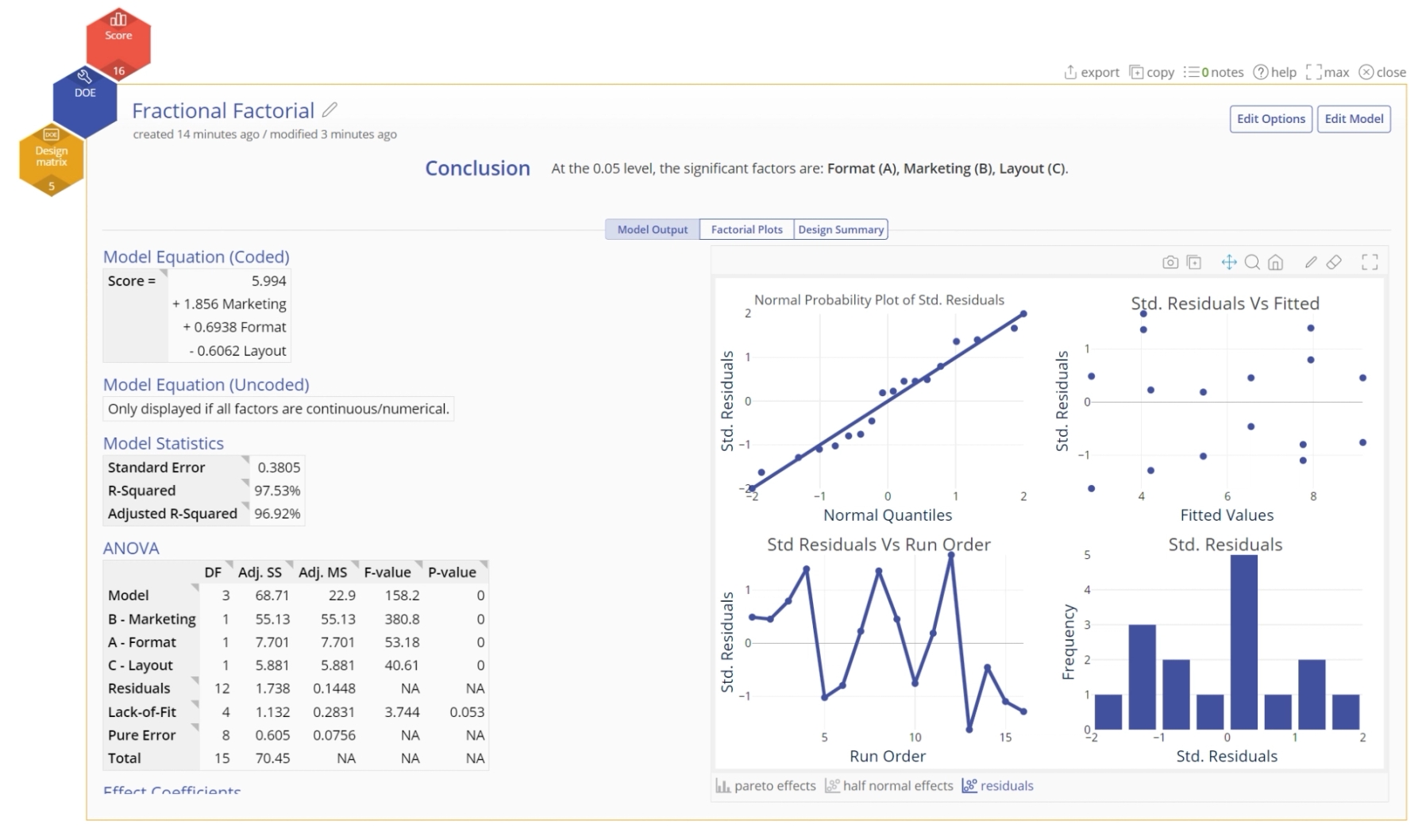
There are additional graphs that can be found on the tabs at the bottom.
Half normal effect plot:
Residuals plot:
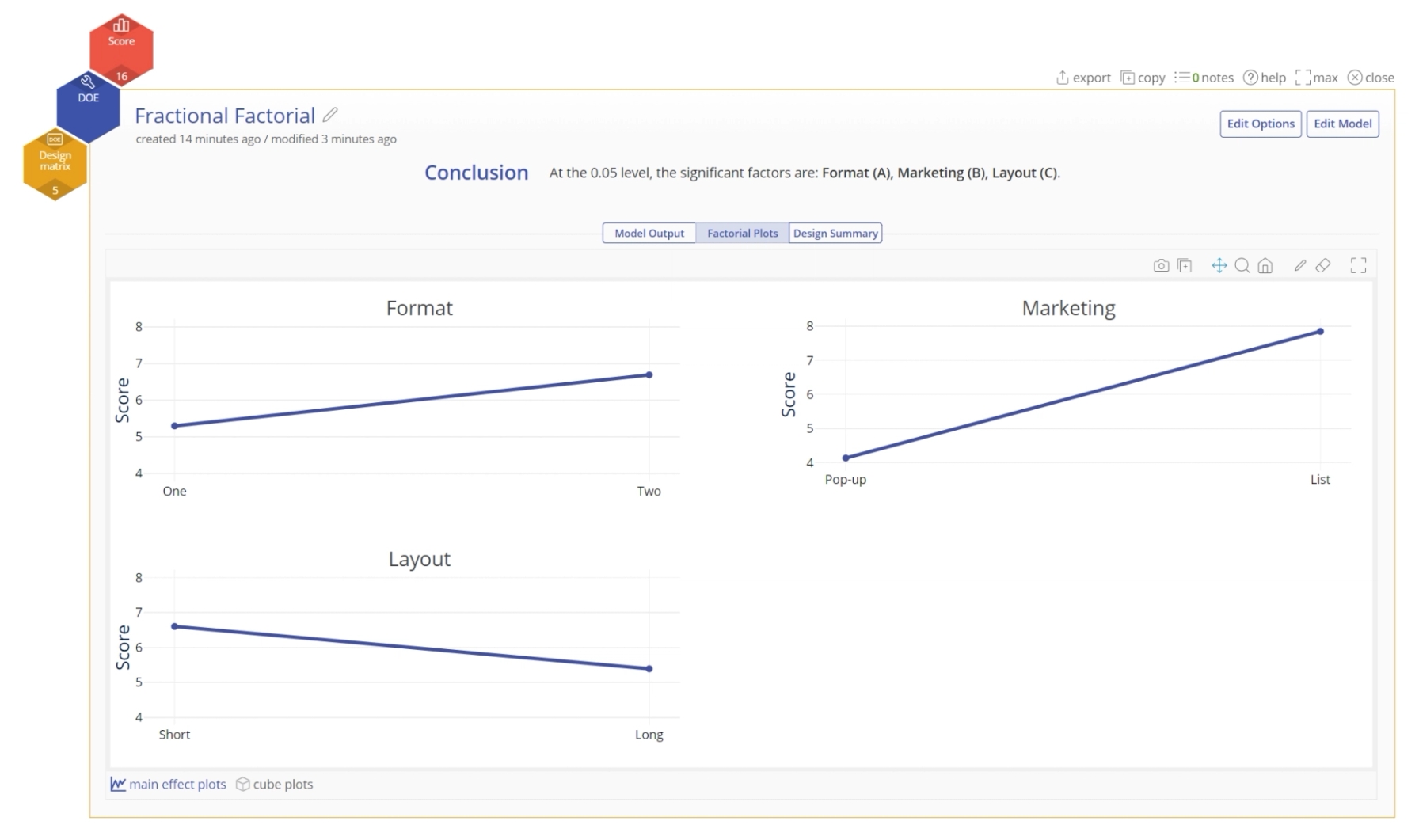
- Click on the Factorial Plots tab to see the charts of main effects and interactions. The main effect plots are shown here; click on the interactions and cube plots buttons at the bottom to see the other charts.
- NOTE: If you have "Show factorial plots for only in model effects" then you will have fewer than all of the effects. Please go to the options to change this if you'd like to see more.
- Click on the Summary tab to see the design summary:
- Select the Edit Model or Edit Options button at the top right of the study to edit the model further or to change any of your previously selected model selection settings:
Push to Optimizer
From here you can use the Push to Optimizer button to optimize the output.
1. Click on the Push to Optimizer button on the top right.
Learn more about the Response Optimizer.
Tutorial
Fractional Factorial DOE Tutorial
Was this helpful?