A Beginner's Guide: What is Lean Six Sigma?
August 30, 2023Lean Six Sigma might sound like a buzzword, but it’s a proven approach to solving complex problems, improving processes, and delivering measurable results. Whether you’re a newcomer exploring process improvement methodologies or a professional wondering how Lean Six Sigma can elevate your career, you’ve come to the right place.
Lean Six Sigma combines two powerful strategies—Lean and Six Sigma—to eliminate waste, reduce defects, and improve efficiency. But how does it work, and where should you begin?
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll break down the basics:
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Why does it matter for businesses and professionals?
- What are the different belt levels and what do they mean?
Whether you’re considering Yellow Belt training as an introduction, Green Belt training to lead projects, or diving into advanced Black Belt techniques, understanding Lean Six Sigma is your first step toward unlocking new opportunities.
This guide will simplify the jargon, give you a clear path forward, and leave you feeling confident about your next move. Ready to get started?
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a team-focused methodology designed to improve organizational performance by eliminating waste and defects. It combines two powerful strategies—Lean and Six Sigma—to create a cohesive approach to problem-solving, making processes more efficient, consistent, and effective.
The Two Pillars of Lean Six Sigma
Lean:
Lean focuses on maximizing value for the customer by eliminating waste in all its forms. The philosophy is simple: anything that doesn’t directly contribute to the bottom line or customer satisfaction is unnecessary. Lean principles aim to streamline workflows and improve overall process flow.
Key Principles of Lean:
- Value: Identify what the customer values most and focus only on activities that enhance it.
- Value Stream: Map out and analyze the complete process to spot inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and non-value-added steps.
- Flow: Create smooth, uninterrupted workflows by minimizing delays, interruptions, and batching.
- Pull: Develop a system where work is driven by actual demand rather than forecasts, ensuring efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of ongoing improvement by eliminating waste and striving for perfection.
Six Sigma:
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that focuses on reducing variability, defects, and errors in processes. It uses statistical analysis and problem-solving techniques to achieve high-quality results and consistency.
Core Elements of Six Sigma:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Use data collected during the Measure and Analyze phases to identify patterns, trends, and root causes of problems.
- Reducing Process Variation: Stabilize and predict processes by minimizing variability, leading to better outcomes.
- Customer-Centric Focus: Prioritize customer needs and ensure that products and services consistently meet their expectations.
Bringing Lean and Six Sigma Together
When combined, Lean Six Sigma offers a powerful framework for driving organizational improvement. Here’s what makes this approach so effective:
- Value to the Customer: Emphasizes understanding and meeting customer needs through feedback and critical-to-quality requirements.
- Improving Business Processes: Identifies waste, streamlines workflows, and optimizes operations using Lean and Six Sigma tools.
- Making Data-Driven Decisions: Relies on data analysis to inform improvements and achieve consistent, measurable outcomes.
- Reducing Process Variation: Applies statistical techniques to control and reduce defects.
- Eliminating Waste: Focuses on the '8 Wastes,' including overproduction, waiting time, excess inventory, and defects.
The Lean Six Sigma Approach
At its core, Lean Six Sigma is a structured, step-by-step way to solve problems and improve processes. It’s about asking the right questions in the right order to uncover solutions that make a real impact. But how do you take these principles and put them into action? That’s where the DMAIC method comes in.
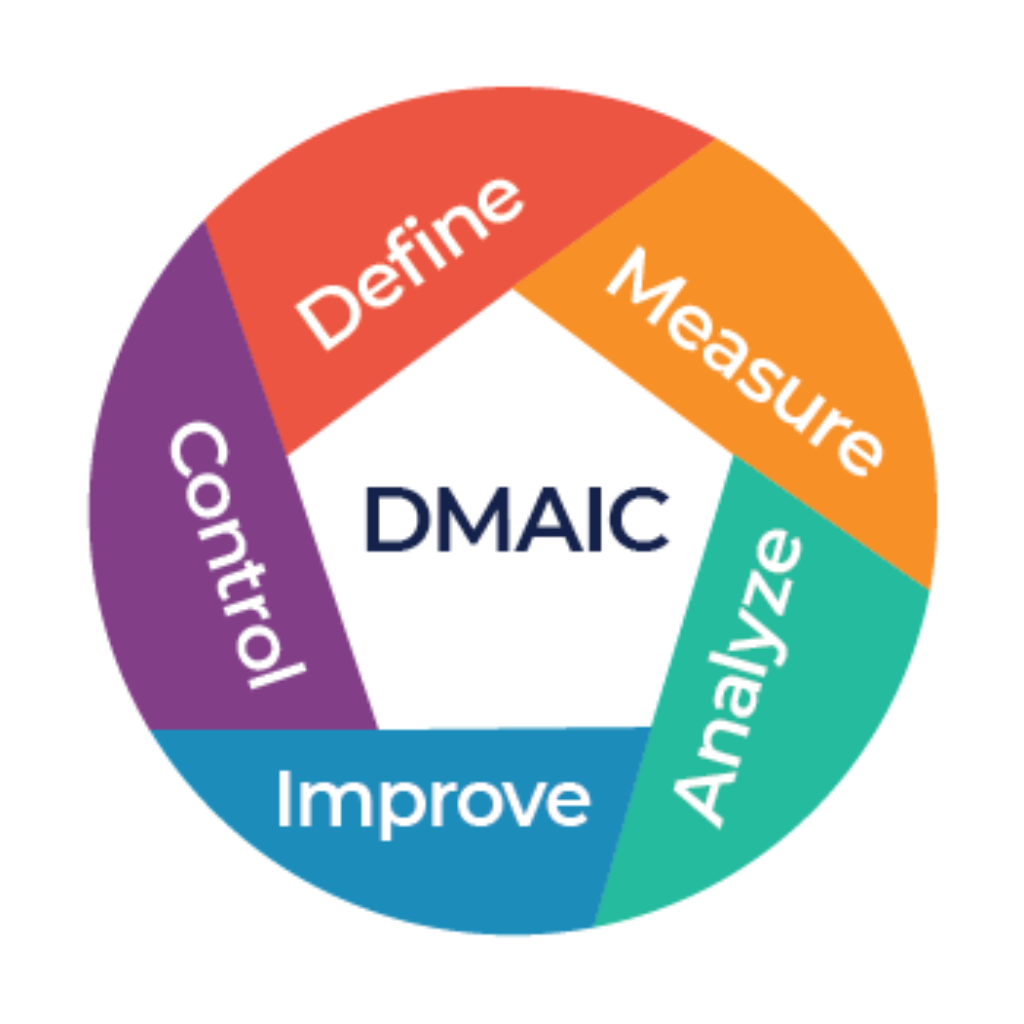
One of the most widely used problem-solving roadmaps in Lean Six Sigma, DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It provides a clear, structured approach to tackling challenges, ensuring teams stay organized and focused on delivering sustainable improvements.
The Five Phases of DMAIC
- Define: Start by clearly defining the problem, setting project goals, and understanding the customer’s needs.
- Measure: Collect data and analyze the current process to understand how it’s performing and identify key metrics.
- Analyze: Use tools and statistical methods to find the root causes of problems or variations in the process.
- Improve: Implement targeted solutions to address the root causes and enhance process performance.
- Control: Put controls in place to maintain the improvements over time and prevent the process from sliding back.
Each phase comes with a set of tools and techniques to make the process smoother and more effective. Here are some examples:
- Gemba Walk: Observe processes firsthand by going to where the work happens to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Pareto Chart: Prioritize problems or causes by visualizing the most significant factors contributing to an issue.
- Root Cause Analysis: Get to the bottom of problems by identifying their underlying causes.
- Kaizen Events: Drive quick, focused improvements through team workshops.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Monitor process stability and performance using data-driven insights.
And that’s just the start! As you build your Lean Six Sigma skills, these tools will become second nature, empowering you to tackle a variety of challenges with confidence.
Want to dive deeper into the DMAIC methodology? Read our blog: What is the DMAIC Methodology?
Why Does Lean Six Sigma Matter for Businesses and Professionals?
Lean Six Sigma stands out because it’s more than just a methodology—it’s a framework for achieving measurable results and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. When implemented effectively, it becomes a cornerstone of success for businesses and individuals alike.
But Lean Six Sigma doesn’t succeed in isolation. For long-term improvements, it requires more than just tools and techniques—it demands a shift in mindset across the organization. Here’s what makes it work:
Teamwork and Collaboration
Improvement isn’t a solo effort. Lean Six Sigma thrives on cross-functional teamwork, where people from different departments come together to solve problems. By engaging stakeholders at all levels and breaking down silos, organizations can drive efficiency and build a culture of collaboration.
Why it matters: Processes don’t exist in isolation, so neither should improvement efforts.
Leadership Engagement
Leaders set the tone for success. Their commitment to Lean Six Sigma ensures that resources are allocated, priorities are clear, and data-driven decision-making becomes the norm. When leadership actively participates, it reinforces the importance of the methodology and inspires buy-in from the entire organization.
Why it matters: Without leadership support, even the best improvement initiatives can lose momentum.
Lean Six Sigma isn’t just about solving problems—it’s about transforming the way businesses operate and empowering professionals to make a lasting impact.
For more on how process improvement drives success across organizations, check out our blog: The Case for Process Improvement
What Are the Lean Six Sigma Belt Levels and What Do They Mean?
Lean Six Sigma uses a belt-level system, inspired by martial arts, to represent increasing levels of expertise and responsibility in process improvement. Each belt level signifies specific knowledge, skills, and roles within Lean Six Sigma projects. The most common belt levels are White, Yellow, Green, Black, and Master Black Belt.
Not everyone needs to aim for the Master Black Belt level—it’s about finding the belt that aligns with your career goals and the challenges you aim to tackle. Here’s what each level represents:
White Belt
- White Belts are introduced to the foundational concepts of Lean Six Sigma. They gain an understanding of basic principles, terminology, and the importance of process improvement. White Belts support Lean Six Sigma efforts by recognizing areas of improvement within their teams but don’t actively lead projects.
Yellow Belt
- Yellow Belts build on the basics with a broader overview of Lean Six Sigma tools and techniques. They are trained to understand how to work within a project team and contribute to improvement initiatives. Yellow Belts participate as team members on Lean Six Sigma projects, supporting Green Belts and Black Belts by gathering data or providing insights into processes.
Green Belt
- Green Belts have a deeper understanding of Lean Six Sigma methodologies and tools. They focus on leading small- to medium-sized projects and implementing solutions within their areas of expertise. Green Belts take on leadership roles within projects, using their training to analyze processes, solve problems, and improve efficiency.
Black Belt
- Black Belts possess advanced knowledge of Lean Six Sigma principles, statistical analysis, and leadership skills. They are responsible for managing large, complex projects and mentoring Green Belts. Black Belts drive significant improvements across organizations by solving high-impact problems, often using advanced techniques like Design of Experiments (DOE) and regression analysis.
Master Black Belt
- Master Black Belts are experts in Lean Six Sigma, with extensive experience in advanced techniques and strategic leadership. They provide training, mentorship, and guidance to Black Belts and project teams while driving organization-wide improvements. Master Black Belts oversee Lean Six Sigma strategy at a high level, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Understanding the Right Lean Six Sigma Certification for You
Each Lean Six Sigma belt level builds on the last, offering unique skills and opportunities to make an impact. The right level for you depends on where you are in your journey and what you want to achieve:
- Just starting out? White or Yellow Belt training provides a solid foundation in Lean Six Sigma principles.
- Looking to lead projects? Green Belt certification equips you with the skills to take charge of improvement initiatives.
- Aiming for senior leadership? Black Belt or Master Black Belt training takes your expertise to the next level, enabling you to drive advanced strategies and lead organizational change.
No matter where you begin, each belt level enhances your ability to deliver value to your organization, making Lean Six Sigma a powerful investment in your professional growth.
Curious about the belt levels and how they compare? Check out our blog to learn more: Lean Six Sigma Belt Levels Explained
Start Your Lean Six Sigma Journey
Lean Six Sigma is more than a methodology—it’s a mindset that helps individuals and organizations solve problems, improve processes, and achieve meaningful results. Whether you’re exploring it for the first time or considering how it fits into your career or business, understanding the basics is the first step toward unlocking its potential.
Ready to dive deeper? Explore our resources like our Green Belt vs Black Belt blog or our Lean Six Sigma Courses to continue your journey.

MoreSteam's Enterprise Process Improvement platform includes the tools, training, and software you need to transform your organization, large or small, into a problem-solving powerhouse. Our products are trusted by over half of the Fortune 500 and by other organizations and universities worldwide. When you partner with MoreSteam you gain a team dedicated to helping you succeed.